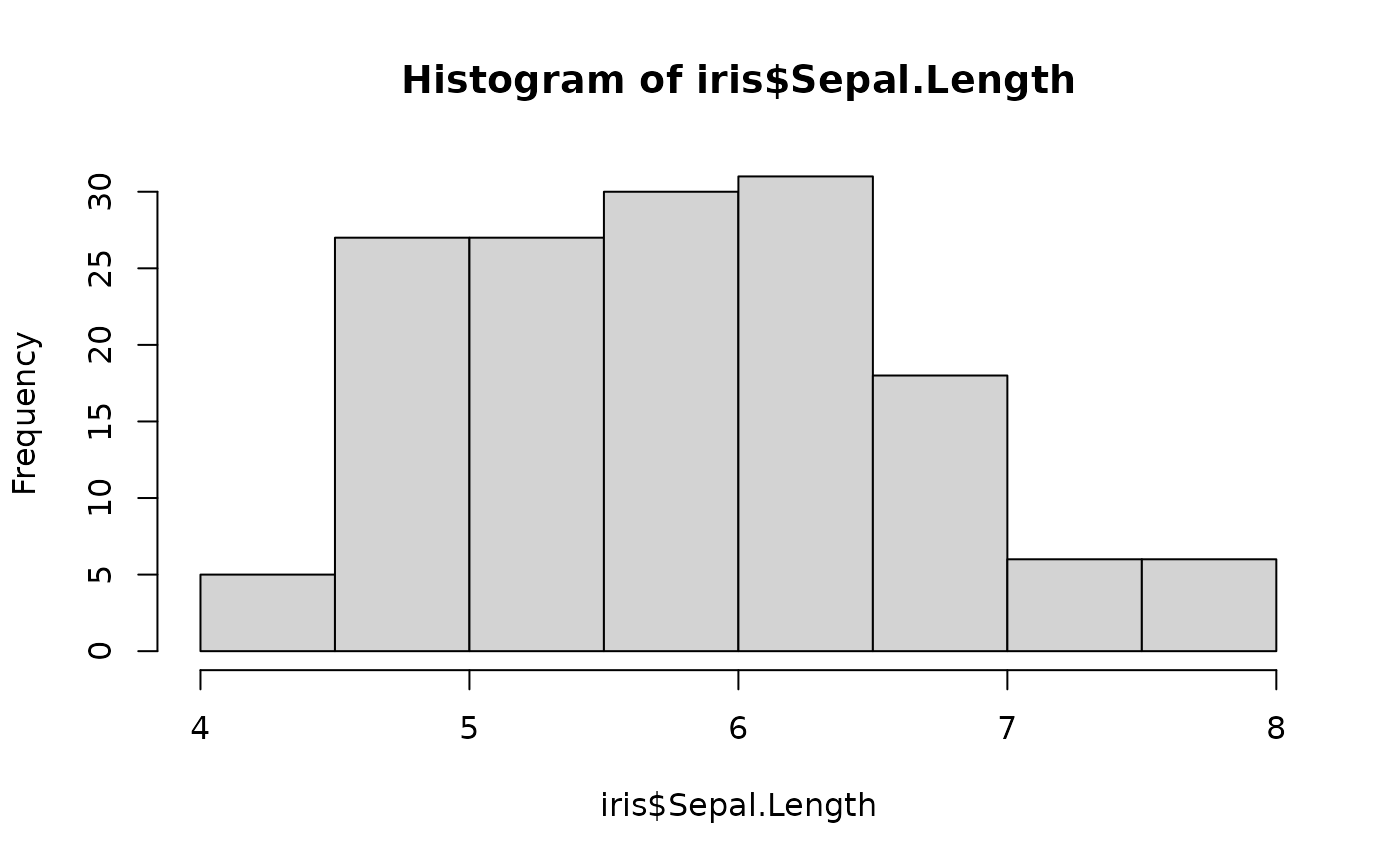
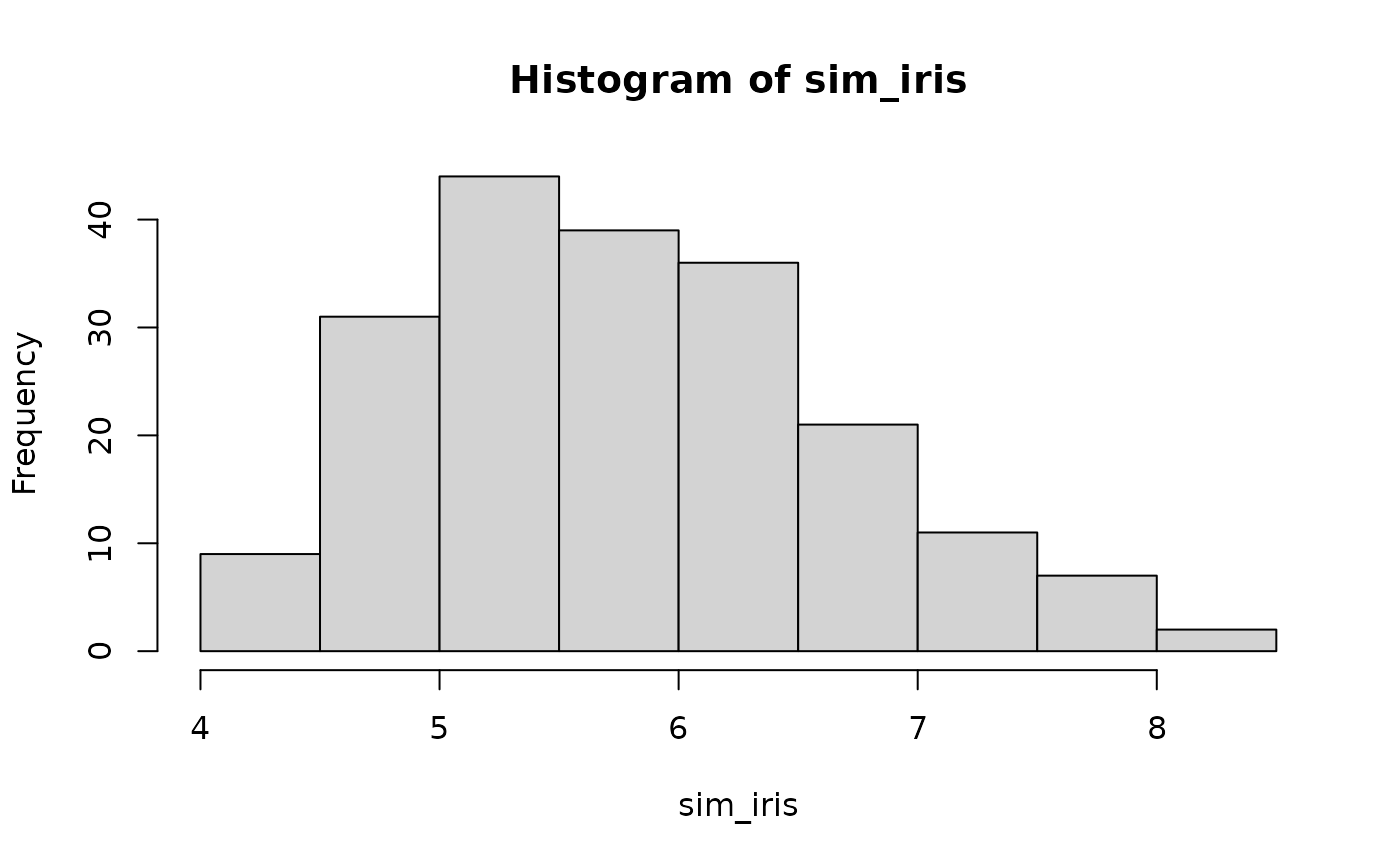
Generate synthetic samples that try to follow an observed distribution by inverting a smooth kernel density estimate (KDE).
Arguments
- x
Numeric vector containing the observed data. Should be numeric or integer. Vector only (no datasets at this stage).
- n
Integer scalar, the number of synthetic samples to generate.
- KDEn
Integer scalar passed to [stats::density()] as the `n` grid size for the KDE; larger values yield a finer grid for integration (default `100`).
- seed
Optional integer to set the random seed for reproducibility.
Details
This utility estimates a univariate density for the input vector, numerically integrates it to obtain a smooth cumulative distribution function (CDF), and then samples synthetic values by inverting that CDF for uniformly distributed probabilities. The result is a set of values that follow the shape of the observed data without reproducing exact observations.
The KDE is fit using [stats::density()] with bandwidth rule `bw = "nrd0"`. The CDF is computed via trapezoidal integration of the KDE on its grid and normalized to \[0, 1\]. An inverse-CDF function is obtained via linear interpolation ([stats::approxfun()]), which is then evaluated at `n` independent uniforms from \[0, 1\].
This approach produces smooth synthetic samples that closely match the observed density.